VMAP (Video Multiple Ad Playlist): Complete Guide for Publishers and Ad Ops
Video Multiple Ad Playlist (VMAP) represents one of the most significant advancements in programmatic video advertising, providing publishers with unprecedented control over ad scheduling and monetization strategies. As video content consumption continues to surge across digital platforms, understanding and implementing VMAP has become essential for publishers seeking to maximize revenue while maintaining optimal user experience.
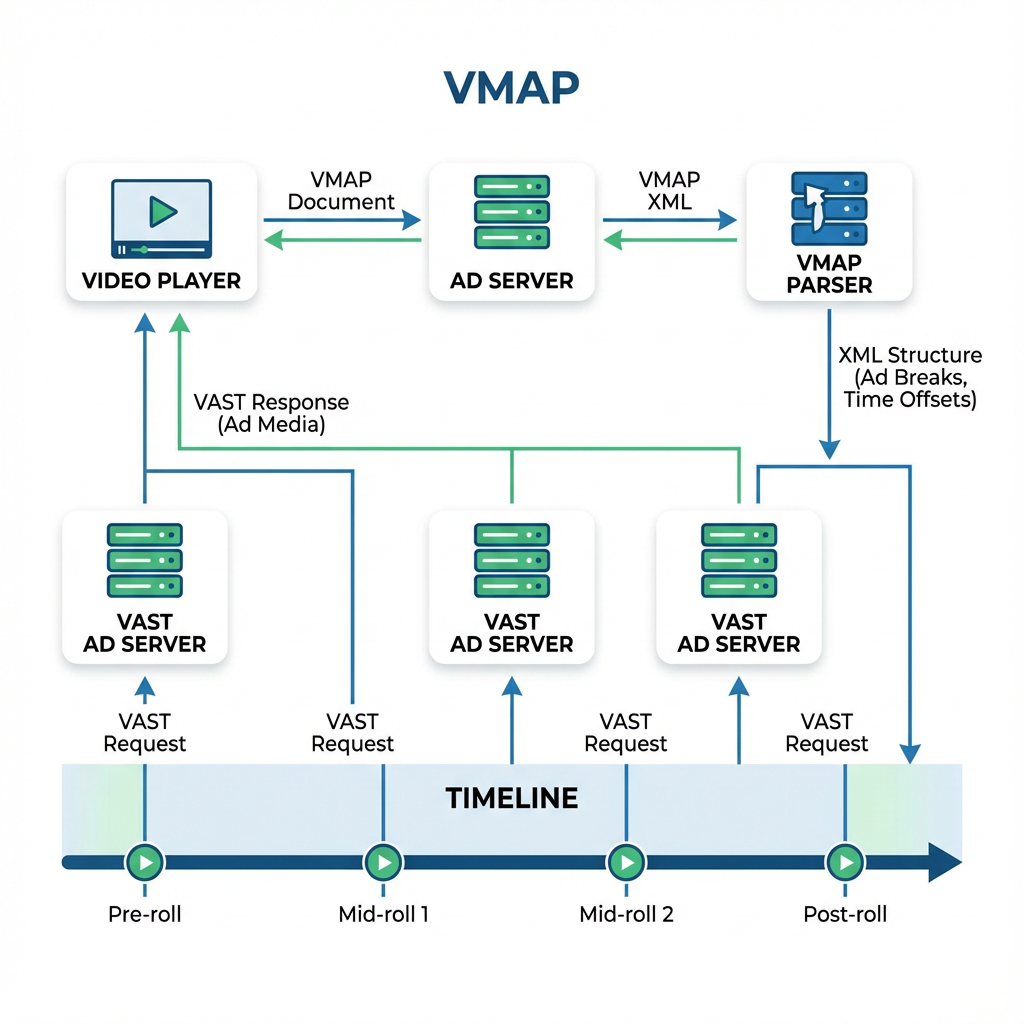
What is VMAP?
VMAP, or Video Multiple Ad Playlist, is an XML-based standard developed by the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) that enables publishers to define when, where, and how many ads should be played during video content. Unlike traditional single-ad implementations, VMAP allows publishers to create comprehensive ad schedules that can include pre-roll, mid-roll, and post-roll advertisements within a single playlist.
The VMAP specification acts as a master playlist that references multiple VAST (Video Ad Serving Template) responses, creating a seamless integration between content and advertising. This approach gives publishers granular control over their ad inventory while providing advertisers with more flexible placement options.
Key Components of VMAP
VMAP documents contain several critical elements that define the ad experience:
- AdBreak elements: Define when ads should play during content
- TimeOffset attributes: Specify exact timing for ad placement
- BreakType parameters: Indicate whether ads are linear or non-linear
- AdSource references: Point to VAST documents containing actual ad creative
- TrackingEvents: Enable measurement and analytics collection
How VMAP Works in Practice
The VMAP Workflow
When a video player requests content, the VMAP workflow follows a structured process:
- Initial Request: The video player requests the VMAP document from the ad server
- Parsing: The player parses the VMAP XML to understand the ad schedule
- Content Preparation: The player prepares to play content while noting scheduled ad breaks
- VAST Requests: At designated times, the player requests VAST documents for specific ad breaks
- Ad Playback: Ads play according to the predefined schedule
- Tracking: Events are fired to measure performance and user engagement
VMAP vs. Traditional Ad Serving
Traditional video ad serving typically requires separate requests for each ad placement, creating potential latency issues and complexity in ad scheduling. VMAP streamlines this process by providing a single document that orchestrates the entire ad experience.
Benefits of VMAP Implementation
Enhanced Revenue Optimization
VMAP enables sophisticated revenue optimization strategies that weren’t possible with single-ad implementations:
Dynamic Ad Density: Publishers can adjust ad frequency based on content length, viewer engagement patterns, or user segments. For example, a 30-minute video might include a pre-roll, three mid-rolls at strategic intervals, and a post-roll, all defined within a single VMAP document.
Flexible Monetization Models: Publishers can implement complex monetization strategies, such as increasing ad density for free content while reducing it for premium subscribers, all managed through VMAP configurations.
Inventory Forecasting: With VMAP, publishers can better predict and package their inventory for advertisers, offering guaranteed placements across multiple positions within video content.
Improved User Experience
Predictable Ad Experience: VMAP allows publishers to create consistent, predictable ad experiences that don’t disrupt content flow. By defining ad breaks at natural content transitions, publishers can maintain viewer engagement while maximizing ad effectiveness.
Reduced Latency: Since the entire ad schedule is defined upfront, video players can pre-fetch ad content and reduce buffering delays, creating smoother transitions between content and advertisements.
Technical Advantages
Simplified Ad Operations: VMAP centralizes ad scheduling logic, reducing the complexity of ad operations and minimizing potential technical issues across different video players and platforms.
Better Analytics and Reporting: With comprehensive tracking built into VMAP documents, publishers gain deeper insights into ad performance across different positions and can optimize accordingly.
Cross-Platform Consistency: VMAP ensures consistent ad experiences across different devices and platforms, which is crucial for publishers distributing content through multiple channels.
VMAP Implementation Best Practices
Strategic Ad Placement
Content-Aware Scheduling: The most effective VMAP implementations consider content structure when scheduling ads. For episodic content, ads should align with natural breaks. For educational content, mid-rolls work best between distinct topics or modules.
Viewer Behavior Analysis: Successful publishers analyze viewer drop-off patterns to optimize ad placement. If data shows significant abandonment after the first mid-roll, adjusting timing or frequency through VMAP can improve both engagement and revenue.
A/B Testing Integration: VMAP supports sophisticated testing scenarios where publishers can serve different ad schedules to various user segments, enabling data-driven optimization of ad density and placement.
Technical Implementation Considerations
Error Handling: Robust VMAP implementations include comprehensive error handling for scenarios where individual VAST responses fail. Publishers should define fallback strategies to ensure ad revenue isn’t lost due to technical issues.
Caching Strategies: Given that VMAP documents orchestrate multiple ad requests, implementing appropriate caching strategies for both VMAP documents and VAST responses can significantly improve performance.
Player Compatibility: While VMAP enjoys broad support, publishers should ensure their chosen video player solution properly implements the full VMAP specification. Modern video player solutions like Veedmo provide comprehensive VMAP support with built-in optimization features.
Revenue Optimization Strategies
Dynamic Ad Insertion: VMAP enables server-side ad insertion (SSAI) implementations where ad content is dynamically inserted into video streams, creating broadcast-quality experiences that are difficult for ad blockers to detect.
Programmatic Integration: Publishers can leverage VMAP to create sophisticated programmatic packages that offer advertisers guaranteed placements across multiple positions, often commanding premium CPMs.
Frequency Capping: VMAP documents can be dynamically generated to respect frequency capping rules, ensuring viewers don’t see the same advertiser too frequently while maximizing fill rates.
Common VMAP Implementation Challenges
Technical Complexity
XML Management: VMAP documents require careful XML structure management. Malformed VMAP documents can break the entire ad experience, making robust testing and validation crucial.
Timing Precision: Accurate ad timing becomes more complex with VMAP, especially for live content or user-generated videos with varying lengths. Publishers need systems that can dynamically adjust ad schedules based on actual content duration.
Cross-Platform Testing: With VMAP enabling complex ad schedules, testing across different devices, browsers, and network conditions becomes more challenging but increasingly important.
Business Considerations
Advertiser Education: Some advertisers may not understand VMAP capabilities, requiring publishers to invest in education and consultation to maximize adoption of premium VMAP-enabled inventory.
Inventory Management: VMAP’s flexibility can create inventory management complexity, particularly when trying to balance guaranteed placements with programmatic fill.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Streaming Platforms
Major streaming platforms leverage VMAP to create television-like ad experiences in digital environments. By scheduling ads at natural content breaks and maintaining consistent timing across episodes, these platforms can command premium advertising rates while providing viewers with familiar experiences.
Educational Content Publishers
Educational publishers use VMAP to monetize longer-form content without disrupting learning experiences. Ads are strategically placed between lessons or modules, and VMAP’s flexibility allows for different ad schedules based on user subscription levels.
Sports and Live Content
Sports publishers implement VMAP for live streaming, using dynamic ad insertion to replace broadcast commercials with targeted digital ads. This approach enables personalization while maintaining the timing expectations viewers have from traditional broadcast experiences.
News and Media Organizations
News organizations leverage VMAP to monetize both live broadcasts and on-demand content. The ability to schedule different ad experiences for breaking news versus feature content helps optimize both revenue and user experience.
Future of VMAP Technology
Emerging Trends
AI-Driven Optimization: Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being applied to VMAP scheduling, automatically optimizing ad placement based on content analysis, viewer behavior, and performance data.
Enhanced Personalization: Future VMAP implementations will likely incorporate more sophisticated audience targeting, creating personalized ad schedules based on individual viewer preferences and behavior patterns.
Interactive Integration: As interactive video advertising evolves, VMAP specifications may expand to support more complex interactive ad experiences while maintaining backward compatibility.
Technical Evolution
Server-Side Enhancement: Server-side ad insertion technologies are becoming more sophisticated, with VMAP playing a crucial role in orchestrating seamless ad experiences that are indistinguishable from original content.
Real-Time Optimization: Future VMAP implementations may support real-time schedule adjustments based on viewer engagement, network conditions, or inventory availability.
Measuring VMAP Success
Key Performance Indicators
Successful VMAP implementations require careful monitoring of several metrics:
Revenue Metrics: Compare overall video ad revenue before and after VMAP implementation, considering both total revenue and revenue per view.
Engagement Metrics: Monitor video completion rates, ad completion rates, and viewer drop-off patterns to ensure VMAP schedules aren’t negatively impacting user experience.
Technical Performance: Track ad loading times, error rates, and cross-platform compatibility to ensure VMAP implementations maintain high technical standards.
Optimization Strategies
Data-Driven Adjustments: Use performance data to continuously refine VMAP schedules, adjusting ad density and placement based on actual viewer behavior and revenue outcomes.
Seasonal Considerations: Implement seasonal VMAP strategies that account for changing viewer behavior and advertiser demand throughout the year.
Conclusion
VMAP represents a fundamental advancement in video advertising technology, offering publishers sophisticated tools for revenue optimization while maintaining high-quality user experiences. As video content consumption continues to grow across all digital platforms, publishers who master VMAP implementation will be better positioned to maximize their advertising revenue.
The key to successful VMAP implementation lies in balancing technical sophistication with user experience considerations. Publishers should focus on content-aware ad placement, robust technical implementation, and continuous optimization based on performance data.
As the digital video landscape continues to evolve, VMAP will likely become even more important for publishers seeking to compete effectively in an increasingly complex advertising ecosystem. Those who invest in understanding and implementing VMAP technology today will be well-positioned for future success in video monetization.